Mixed Bed ION Exchange Demineralisation
Mixed bed resin consists of Strong Acid Cation Resin (SAC) and Strong Base Anion Resin (SBA) and are used to purify water.
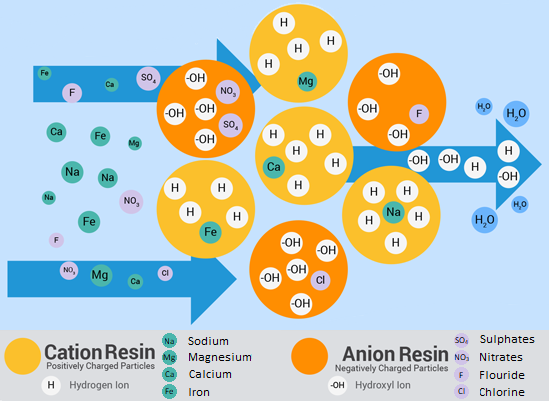
Strong Acid Cation Resin is supplied in the Hydrogen form (H), which it exchanges with Cations such as Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium and Iron etc.
Strong Base Anion Resin is supplied in the Hydroxide form (OH), which it exchanges with Anions such as Sulphates, Nitrates, Flouride and Chloride etc.
The H and OH that are released, combine to form pure water H2O.
Typically mixed bed resin consists of 40% SAC to 60% SBA, this is because of the different exchange capacity of the two resin types.
The mixed bed can be used on tap water to give good quality water for emergency or backup processes, however, due to the high Cation/Anion loading of tap water, the mixed bed would soon exhaust its capacity.
Usually, a mixed bed is used after an Ion Exchange Demineraliser or Reverse Osmosis system to ‘polish’ the water. Used in this way, the mixed bed is capable of producing high quality, almost pure water up to 18.2Mohm, whilst still giving a high capacity and lasting for several months (depending on the size of vessels).
When using mixed bed resin with an RO, the capacity of the resin can be severely impacted by CO2 in the RO permeate. This CO2 does not show up on the RO conductivity probe, but will be removed by the Anion resin reducing the overall lifespan of the mixed bed. This is also true when mixed bed is used to polish a ring main system and CO2 is picked up by the water in the tank.
Lubron are able to provide mixed bed units in various sizes, with a simple built in moving needle resistivity meter that lets you know when your resin is exhausted.
Alternatively, we can supply resistivity probes with 0-10v or 4-20mA outputs to allow you to interface to a PLC or BMS system.
Resin changes can be carried out on site by our fully trained in-house engineering team, or you can send spent vessels to our factory to be emptied and refilled with fresh resin before returning them.
If you would like to find out more about our mixed bed ion exchange demineralisation, get in contact with a friendly advisor today.

FAQ's
How do i remove Silica from water?
Silica in water comes in two distinct forms, Colloidal Silica which needs to be filtered out using physical filtration methods and reactive Silica. Mixed beds are an excellent way to remove reactive Silica from water, especially when ‘polishing’ after an RO plant.

